Provisioning cloud resources
In this section, we will replace the in-memory database being used by carts with DynamoDB. We will do this by composing a WebApplicationDynamoDB ResourceGraphDefinition that builds on the base WebApplication template.
First, let's delete the kro instance we created in the previous section:
webapplication.kro.run "carts" deleted
This will clean up all the associated resources:
No resources found in carts namespace.
Now let's examine the ResourceGraphDefinition template that defines the reusable WebApplicationDynamoDB API:
Expand for full RGD manifest
apiVersion: kro.run/v1alpha1
kind: ResourceGraphDefinition
metadata:
name: web-application-ddb
spec:
schema:
apiVersion: v1alpha1
kind: WebApplicationDynamoDB
spec:
appName: string | required=true description="Web Application Name"
replicas: integer | default=1 minimum=1 maximum=100
image: string | default=nginx
port: integer | default=8080
dynamodb:
tableName: string | required=true description="DynamoDB Table Name"
healthcheck:
readinessPath: string | default="/actuator/health/readiness"
readinessPort: integer | default=8080
livenessPath: string | default="/actuator/health/liveness"
livenessPort: integer | default=8080
service:
enabled: boolean | default=true
aws:
accountID: integer | required=true
region: string | default="us-west-2"
env: map[string]string | default={}
ingress:
enabled: boolean | default=false
path: string | default="/"
healthcheckPath: string | default="/health"
groupname: string | default="eks-workshop"
resources:
- id: podIdentityAssociation
template:
apiVersion: eks.services.k8s.aws/v1alpha1
kind: PodIdentityAssociation
metadata:
name: ${schema.spec.appName}
namespace: ${schema.spec.appName}
spec:
clusterName: "eks-workshop"
namespace: ${schema.spec.appName}
serviceAccount: ${schema.spec.appName}
roleARN: ${itemsTableIAMRole.status.ackResourceMetadata.arn}
- id: webApplication
template:
apiVersion: kro.run/v1alpha1
kind: WebApplication
metadata:
name: ${schema.spec.appName}
namespace: ${schema.spec.appName}
spec:
appName: ${schema.spec.appName}
replicas: 1
image: ${schema.spec.image}
port: 8080
healthcheck:
readinessPath: ${schema.spec.healthcheck.readinessPath}
readinessPort: ${schema.spec.healthcheck.readinessPort}
livenessPath: ${schema.spec.healthcheck.livenessPath}
livenessPort: ${schema.spec.healthcheck.livenessPort}
service:
enabled: ${schema.spec.service.enabled}
iamRole: ${podIdentityAssociation.status.ackResourceMetadata.arn}
env: ${schema.spec.env}
ingress:
enabled: ${schema.spec.ingress.enabled}
path: ${schema.spec.ingress.path}
healthcheckPath: ${schema.spec.ingress.healthcheckPath}
groupname: ${schema.spec.ingress.groupname}
- id: serviceDDB
template:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: carts-dynamodb
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/created-by: eks-workshop
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 8000
targetPort: dynamodb
protocol: TCP
name: dynamodb
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ${schema.spec.appName}
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ${schema.spec.appName}
app.kubernetes.io/component: dynamodb
- id: itemsTable
template:
apiVersion: dynamodb.services.k8s.aws/v1alpha1
kind: Table
metadata:
name: items
namespace: ${schema.spec.appName}
spec:
keySchema:
- attributeName: id
keyType: HASH
attributeDefinitions:
- attributeName: id
attributeType: "S"
- attributeName: customerId
attributeType: "S"
billingMode: PAY_PER_REQUEST
tableName: ${schema.spec.dynamodb.tableName}
globalSecondaryIndexes:
- indexName: idx_global_customerId
keySchema:
- attributeName: customerId
keyType: HASH
- attributeName: id
keyType: RANGE
projection:
projectionType: "ALL"
- id: itemsTableIamPolicy
template:
apiVersion: iam.services.k8s.aws/v1alpha1
kind: Policy
metadata:
name: ${itemsTable.spec.tableName}-iam-policy
spec:
name: ${itemsTable.spec.tableName}-iam-policy
description: "EKS Workshop Carts DynamoDB Policy"
policyDocument: >
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllAPIActionsOnCart",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "dynamodb:*",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:dynamodb:${schema.spec.aws.region}:${schema.spec.aws.accountID}:table/${itemsTable.spec.tableName}",
"arn:aws:dynamodb:${schema.spec.aws.region}:${schema.spec.aws.accountID}:table/${itemsTable.spec.tableName}/index/*"
]
}
]
}
- id: itemsTableIAMRole
template:
apiVersion: iam.services.k8s.aws/v1alpha1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: ${itemsTable.spec.tableName}-iam-role
namespace: ${schema.spec.appName}
spec:
name: ${itemsTable.spec.tableName}-iam-role
description: "EKS Workshop Carts DynamoDB Role"
maxSessionDuration: 3600
policies:
- ${itemsTableIamPolicy.status.ackResourceMetadata.arn}
assumeRolePolicyDocument: >
{
"Version":"2012-10-17",
"Statement": [{
"Effect":"Allow",
"Principal": {"Service": "pods.eks.amazonaws.com"},
"Action": [
"sts:TagSession",
"sts:AssumeRole"
]
}]
}
This ResourceGraphDefinition:
- Creates a custom
WebApplicationDynamoDBAPI that composes the WebApplication RGD - Provisions a DynamoDB table with ACK
- Creates IAM roles and policies for DynamoDB access
- Configures EKS Pod Identity for secure access from application pods
To learn more about EKS Pod Identity, refer to the official documentation.
Notice how this RGD includes the WebApplication RGD in its resources section. By referencing webApplication, this template reuses all the Kubernetes resources defined in the base WebApplication RGD while adding DynamoDB, IAM, and Pod Identity resources.
Let's apply the ResourceGraphDefinition to register the WebApplicationDynamoDB API:
resourcegraphdefinition.kro.run/web-application-ddb created
This registers the WebApplicationDynamoDB API. Verify the Custom Resource Definition (CRD):
NAME CREATED AT
webapplicationdynamodbs.kro.run 2024-01-15T10:35:00Z
Now let's examine the carts-ddb.yaml file that will use the WebApplicationDynamoDB API to create an instance of the Carts component:
apiVersion: kro.run/v1alpha1
kind: WebApplicationDynamoDB
metadata:
name: carts
namespace: carts
spec:
# Basic types
appName: carts
replicas: 1
image: "public.ecr.aws/aws-containers/retail-store-sample-cart:1.2.1"
port: 8080
dynamodb:
tableName: "eks-workshop-carts-kro"
env:
RETAIL_CART_PERSISTENCE_PROVIDER: "dynamodb"
RETAIL_CART_PERSISTENCE_DYNAMODB_TABLE_NAME: "eks-workshop-carts-kro"
aws:
accountID: ${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}
region: ${AWS_REGION}
Uses the custom WebApplicationDynamoDB API created by our RGD
Creates a resource named carts in the carts namespace
Specifies the application name for resource naming
Sets single replica
Uses the retail store cart service container image
Exposes the application on port 8080
Specifies the DynamoDB table name
Sets environment variables to enable DynamoDB persistence mode
Provides AWS account ID and region for IAM and Pod Identity configuration
Next, let's deploy the updated component leveraging the carts-ddb.yaml file:
webapplicationdynamodb.kro.run/carts created
kro will process this custom resource and create all the underlying resources including the DynamoDB table. Let's verify the custom resource was created:
NAME STATE SYNCED AGE
carts IN_PROGRESS False 16s
Now we can wait until the instance has reached a "synced" state:
To verify that the DynamoDB table has been created, we can check the generated ACK resource:
table.dynamodb.services.k8s.aws/items condition met
ACTIVE
Let's confirm that the table has been created using the AWS CLI:
{"TableNames": [
"eks-workshop-carts-kro"
]
}
Our DynamoDB table and component have been successfully created using kro's composable approach.
To verify that the component is working with the new DynamoDB table, we can interact with it through a browser. An NLB has been created to expose the sample application for testing:
http://k8s-ui-ui-a9797f0f61.elb.us-west-2.amazonaws.com
Please note that the actual endpoint will be different when you run this command as a new Network Load Balancer endpoint will be provisioned.
To make sure the load balancer has finished provisioning, you can run this command:
Once the load balancer is provisioned, you can access it by pasting the URL in your web browser. You'll see the UI from the web store displayed and will be able to navigate around the site as a user.
To verify that the Carts module is indeed using the DynamoDB table we just provisioned, try adding a few items to the cart.
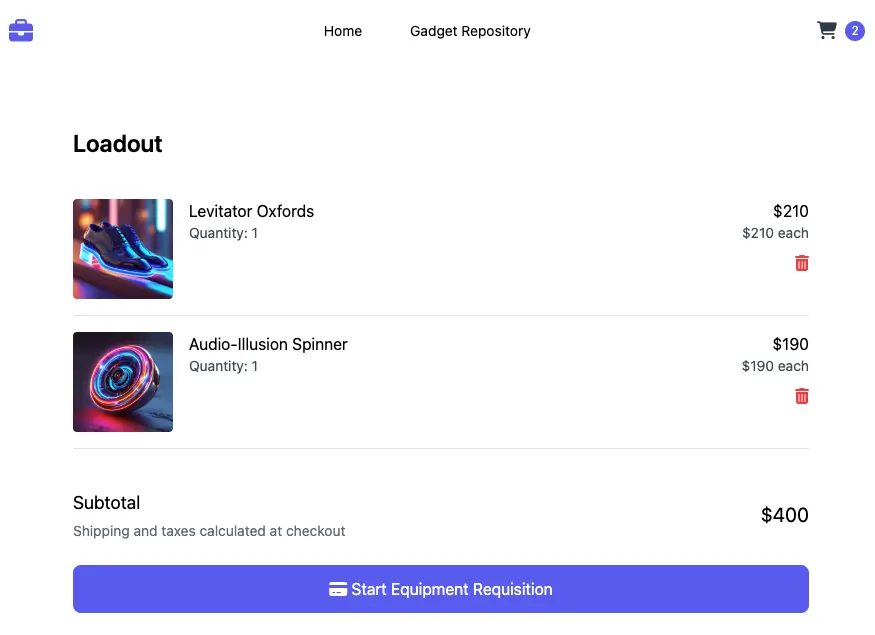
To confirm that these items are also in the DynamoDB table, run:
Congratulations! We have successfully demonstrated kro's composability by building on the base WebApplication template to add DynamoDB storage.